Calculate your estimated 2025 Canadian income tax using our comprehensive guide, incorporating the latest available federal tax bracket information. This guide also provides an overview of provincial taxes and other factors that may influence your total tax bill.
Last updated October 26, 2024
Disclaimer: This guide is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional tax advice. Consult a qualified tax professional for personalized advice.
Understanding Federal Income Tax
Canada’s federal income tax system uses a marginal tax rate structure. This means different portions of your income are taxed at different rates, like climbing a staircase where each step represents a different tax bracket. The higher your income, the higher the rate you may pay on the portion of your income that falls within higher tax brackets, not your entire income.
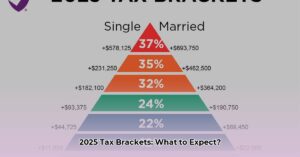
The 2025 federal tax brackets are as follows:
| Taxable Income | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $57,375 | 15% |
| $57,376 to $114,750 | 20.5% |
| $114,751 to $177,882 | 26% |
| $177,883 to $253,414 | 29% |
| Over $253,415 | 33% |
Example: If your taxable income is $80,000, the first $57,375 is taxed at 15%, and the remaining $22,625 is taxed at 20.5%.
The Basic Personal Amount (BPA)
The Basic Personal Amount (BPA) is a non-refundable tax credit that reduces the amount of your income subject to federal tax. For 2025, the BPA is $16,129, but this amount decreases for higher earners, with a minimum of $14,538. This means a portion of your income is automatically tax-free. Remember, this is for federal tax only. Each province also has its own BPA with its own set of rules.
Provincial and Territorial Taxes
Provincial and territorial taxes are calculated separately from federal taxes and represent a significant portion of your total income tax bill. Each province/territory has its own unique tax rates, brackets, and rules. It is essential to consult your province or territory’s website for specific information.
Other Deductions and Credits
Various deductions and credits can further reduce your taxable income. Some common examples include Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) contributions, charitable donations, and certain medical expenses. Exploring these options can potentially lower your overall tax burden.
Calculating Your Total Income Tax
Estimating your total 2025 income tax involves combining your federal and provincial taxes:
- Calculate Federal Tax: Use the federal tax brackets and the BPA to estimate your federal tax.
- Calculate Provincial Tax: Research your province or territory’s tax rates and BPA, and calculate your provincial tax based on your income and applicable deductions.
- Add Federal and Provincial Taxes: The sum of your estimated federal and provincial taxes represents your estimated total income tax.
Tax Software and Professional Advice
Tax software can streamline the calculation process and help identify potential deductions. For more complex situations, or if you’re unsure about any aspect of your taxes, consulting a qualified tax professional is highly recommended.
Updates and Changes
Tax laws and regulations are subject to change. Stay informed about updates from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) to ensure you have the most accurate information.
FAQ
- What if my income changes during the year? Your tax is calculated based on your total income for the entire year.
- What are common tax deductions? RRSP contributions, charitable donations, and certain medical expenses are common deductions. However, eligibility criteria may apply.
- Where can I find my provincial tax information? Visit the website of your province or territory for specific tax rates and rules.
Conclusion
Understanding how Canadian income tax works allows you to plan your finances effectively. While this guide helps estimate your 2025 taxes, consulting a tax professional is always recommended for personalized advice. As 2025 approaches, remember to verify the final tax rates and regulations on the official CRA website for the most accurate calculation.