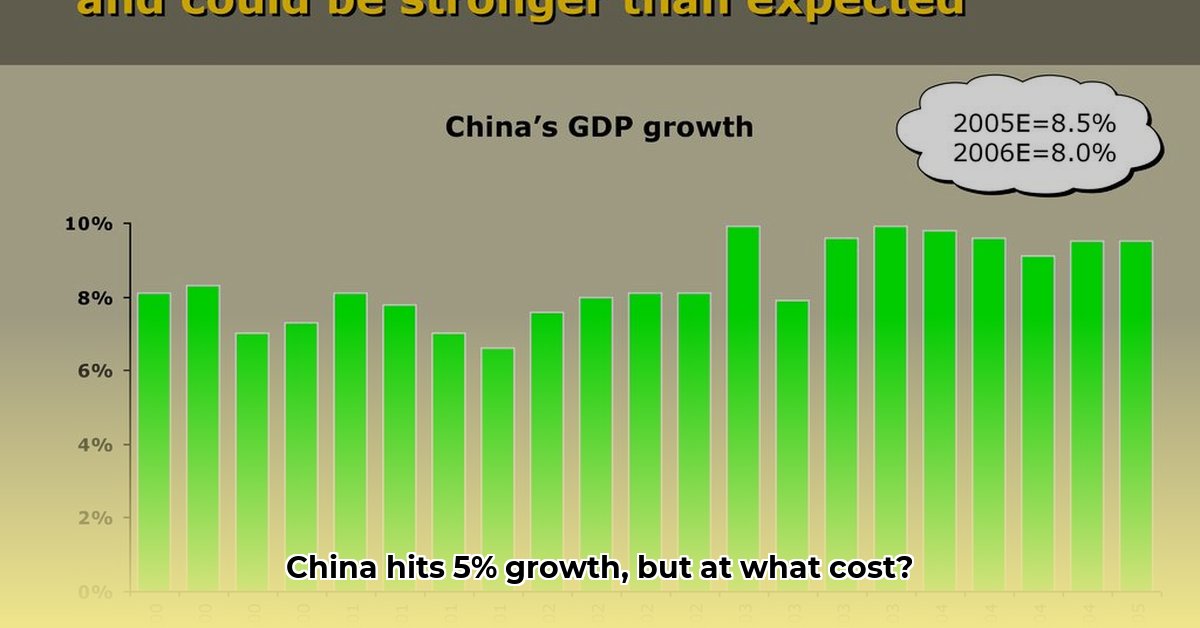
China announced its economy grew by 5% in 2024, meeting its official target. But this seemingly positive headline masks a more complex reality. This analysis delves beyond the surface, examining the factors driving this growth, the underlying challenges, and the potential risks ahead.
Decoding China’s 5% Growth: A Mixed Bag
While the 5% figure suggests stability, the details reveal a mixed bag. A surge in exports, likely driven by businesses front-loading shipments in anticipation of US tariffs, contributed significantly. Simultaneously, government stimulus measures, including interest rate cuts and infrastructure spending, provided a short-term boost. However, these measures raise questions about the sustainability of this growth trajectory.
Unpacking the Drivers: Exports and Stimulus
The 7.1% surge in exports provided substantial momentum. This, however, likely reflects a temporary acceleration rather than sustained growth, as businesses probably rushed shipments to avoid potential tariff hikes. The Economist frequently highlights the risks of export-dependent growth models.
Government stimulus, reminiscent of strategies discussed by Paul Krugman, offered a short-term boost but its long-term impact remains unclear. While infrastructure investments can spur growth, excessive reliance on such measures can lead to inflationary pressures and unsustainable debt levels.
Underlying Weaknesses: A Cause for Concern
Several underlying weaknesses persisted throughout 2024. Consumer spending remained sluggish, growing by a mere 3.5%, a worrying sign for the health of domestic demand. Deflationary pressures emerged, posing a threat to business profitability and investment. The struggling property sector continued to drag down growth, while the looming demographic challenge of a shrinking and aging population casts a long shadow over future economic prospects. These challenges are akin to those faced by other developed economies, as analyzed by the Financial Times.
Data Discrepancies: A Question of Accuracy
The official 5% growth figure has been met with skepticism. Some analysts point to the massive stimulus package, uneven growth across sectors, and deflationary pressures as evidence that the actual growth might be lower. Independent estimates suggest a more modest growth of 2.4% to 2.8%. This discrepancy raises concerns about the reliability of official data and its potential impact on policy decisions.
The Stimulus Question: Masking Weakness?
The massive $1.36 trillion stimulus package raises questions about whether it artificially inflated growth figures. While stimulus can provide a temporary boost, some economists argue it may mask underlying structural weaknesses, delaying necessary reforms. Did this stimulus provide genuine momentum or create a mirage of economic health? The answer remains elusive.
Beyond the Numbers: Anecdotal Evidence
Anecdotal evidence, including reports of job losses and wage cuts, paints a different picture than the official narrative. While not statistically representative, these accounts offer valuable insights into the lived experiences of ordinary Chinese citizens, further fueling concerns about the true state of the economy.
The Road Ahead: Navigating Uncertainty
China’s economic future remains uncertain. The combination of export dependence, government intervention, and structural weaknesses creates a complex and potentially volatile situation. The effectiveness of government efforts to boost domestic consumption remains to be seen.
Long-Term Challenges: Structural Reforms and Demographics
China faces significant long-term challenges, including the need for structural reforms to address inefficiencies and the looming demographic shift of a shrinking workforce. These challenges require comprehensive and sustained efforts. Ongoing research suggests these structural factors could significantly impact China’s future growth trajectory.
Geopolitical Risks: Trade and Technology
Geopolitical tensions, particularly with the US, add another layer of complexity. Trade disputes and technological competition create an unpredictable environment, discouraging investment and hindering long-term planning. These external pressures add to the uncertainties surrounding China’s economic outlook.
| Key Economic Indicator | 2024 Performance | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | 5% (official) | Questions about accuracy and sustainability |
| Exports | 7.1% growth | Likely driven by temporary factors |
| Consumer Spending | 3.5% growth | Weak domestic demand |
| Property Market | Downturn | Drag on overall growth |
| Inflation | Deflationary | Concerns about economic weakness |
| Stimulus | $1.36 trillion | Potential for masking structural issues |
In conclusion, while China officially met its 5% GDP growth target in 2024, the underlying reality is far more nuanced. The growth appears largely driven by temporary factors, while significant challenges persist. The coming years will be crucial for China to address these challenges and navigate the uncertainties ahead. The true trajectory of China’s economy remains to be seen, and ongoing analysis and research will be essential for understanding the unfolding narrative.